[New Updated Questions] Free Microsoft 70-341 PDF MCSE2003 Messaging Youtube Study with The Knowledge And Skills
In order to meet the needs of each candidate, the team of IT experts in Pass4itsure are using their experience and knowledge to improve the quality of exam training materials constantly. We can guarantee that you can pass the Pass4itsure 70-341 pdf the first time. If you buy the goods of Pass4itsure, then you always be able to get newer and more accurate test information.
Exam Code: 70-341
Exam Name: Core Solutions of Microsoft Exchange Server 2013
Updated: May 29, 2017
Q&As: 204
Exam Information: https://www.pass4itsure.com/70-341.html
The coverage of the products of Pass4itsure is very broad. It can be provide convenient for a lot of candidates who participate in IT certification exam. Its accuracy rate is 100% and let you take the Pass4itsure 70-341 pdf with peace of mind, and pass the exam easily.
Share some Microsoft Specialist 70-341 PDF Exam Questions and Answers Below:
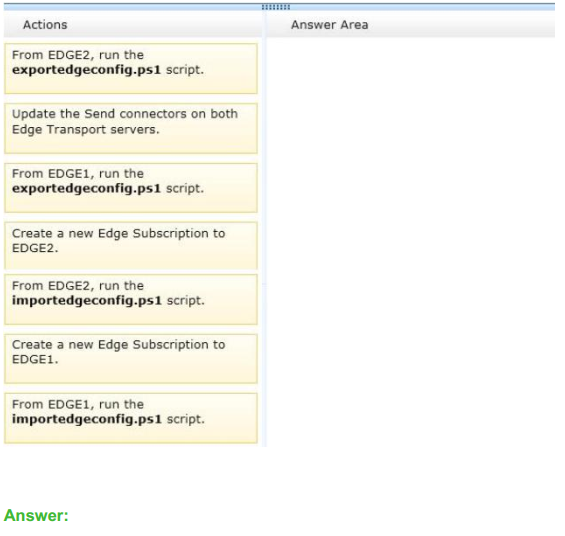
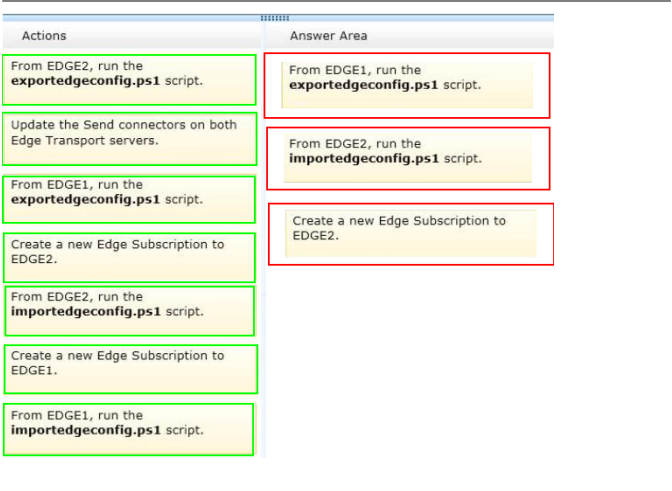
Question No : 5 DRAG DROP – (Topic 1)
You are evaluating the implementation of a second Edge Transport server named EDGE2
in the Amsterdam office.
You need to recommend which tasks must be performed to ensure that email messages
can be sent by the organization if a single Edge Transport server fails.
Which three actions should you include in the recommendation? To answer, move the three appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area
and arrange them in the correct order.
Question No : 6 – (Topic 1) You need to recommend which type of group must be used to create the planned
department lists.
Which type of group should you recommend?
A. Universal Distribution
B. Dynamic Distribution
C. Global Security
D. Universal Security
Answer: A
Explanation:
There are two types of groups that can be used to distribute messages:
Mail-enabled universal distribution groups (also called distribution groups) can be used only
to distribute messages.
Mail-enabled universal security groups (also called security groups) can be used to
distribute messages as well as to grant access permissions to resources in Active Directory. For more information, see Manage Mail-Enabled Security Groups.
A mail-enabled security group is an Active Directory universal security group object that
can be used to assign access permissions to resources in Active Directory and can also be
used to distribute messages.
It’s important to note the terminology differences between Active Directory and Exchange.
In Active Directory, a distribution group refers to any group that doesn’t have a security
context, whether it’s mail-enabled or not. In contrast, in Exchange, all mail-enabled groups
are referred to as distribution groups, whether they have a security context or not.
Dynamic Distribution Groups
Unlike regular distribution groups that contain a defined set of members, the membership
list for dynamic distribution groups is calculated each time a message is sent to the group,
based on the filters and conditions that you define. When an email message is sent to a
dynamic distribution group, it’s delivered to all recipients in the organization that match the
criteria defined for that group.
Manage Distribution Groups: Exchange Online Help
Question No : 7 – (Topic 1) You need to recommend which tasks must be performed to meet the technical
requirements of the research and development (R&D) department.
Which two tasks should you recommend? (Each correct answer presents part of the
solution. Choose two.)
A. Create a new global address list (GAL) and a new address book policy.
B. Modify the permissions of the default global address list (GAL), and then create a new
GAL.
C. Run the Update AddressList cmdlet.
D. Run the Set-Mailbox cmdlet.
E. Create an OAB virtual directory.
Answer: A,D
Explanation:
NOT B
Need an address book policy NOT C
Update AddressList cmdlet
Use the Update-AddressList cmdlet to update the recipients included in the address list that
you specify.
EXAMPLE 1
This example updates the recipients of the address list building4 and under the container
All Users\Sales.
Update-AddressList -Identity “All Users\Sales\building4”
NOT E
Will not resolve the issue
Need an address book policy and to assign this policy to users.
A
Address book policies (ABPs) allow you to segment users into specific groups to provide
customized views of your organization’s global address list (GAL).
When creating an ABP, you assign a GAL, an offline address book (OAB), a room list, and
one or more address lists to the policy.
You can then assign the ABP to mailbox users, providing them with access to a customized
GAL in Outlook and Outlook Web App.
The goal is to provide a simpler mechanism to accomplish GAL segmentation for on
premises organizations that require multiple GALs.
D
After you create an address book policy (ABP), you must assign it to mailbox users. Users
aren’t assigned a default ABP when their user account is created.
If you don’t assign an ABP to a user, the global address list (GAL) for your entire
organization will be accessible to the user through Outlook and Outlook Web App.
This example assigns the ABP All Fabrikam to the existing mailbox user
[email protected].
Set-Mailbox -Identity [email protected] -AddressBookPolicy “All Fabrikam”
Address Book Policies: Exchange Online Help
Set-Mailbox: Exchange 2013 Help
Question No : 8 – (Topic 1)
You are testing the planned implementation of Domain Security.
You discover that users fail to exchange domain-secured email messages.
You open the Exchange Management Shell and discover the output shown in the exhibit.
(Click the Exhibit button.)
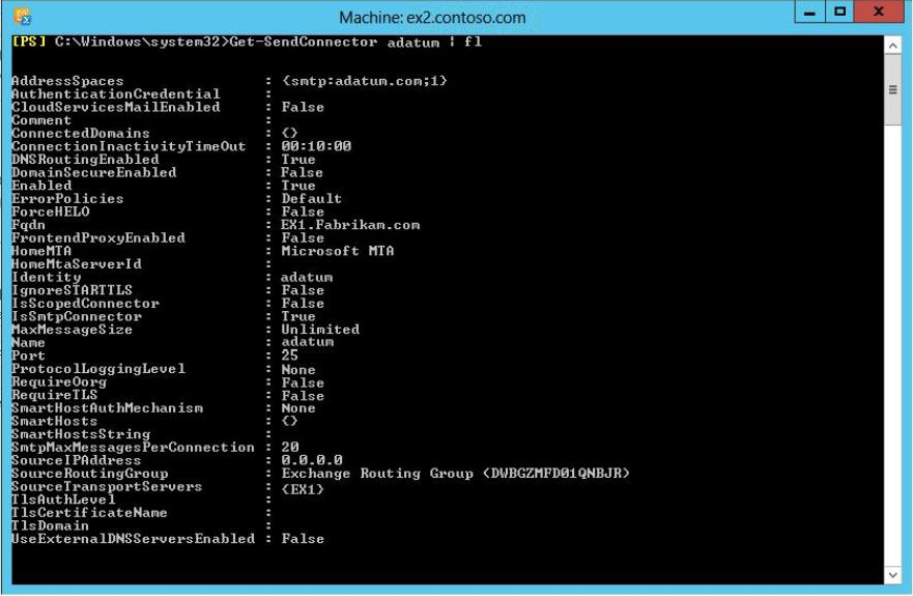
You need to ensure that users can exchange email messages by using Domain Security.
Which two parameters should you modify by using the Set-SendConnector cmdlet? (Each
correct answer presents part of the solution. Choose two.)
A. tlsauthlevel
B. requiretls
C. ignorestarttls
D. tlsdomain
E. domainsecureenabled
F. smarthostauthmechanism
Answer: B,E
Explanation:
Domain Security
Domain Security is a feature of Exchange Server (both 2010 and 2013) that can secure
SMTP traffic between two Exchange organizations.
It is implemented on server level, and it works without configuring any options on user
(sender or recipient) side. Domain Security uses mutual TLS authentication to provide
session-based authentication and encryption.
Mutual TLS authentication is different from TLS as it’s usually implemented. Usually, when
you implement TLS, client will verify the server certificate, and authenticate the server,
before establishing a connection.
With mutual TLS authentication, each server verifies the connection with the other server
by validating a certificate that’s provided by that other server, so clients are not included at
all.
We establish secure SMTP channel between two Exchange Servers, usually over the
Internet.
Clients, Outlook and Outlook Web App, will be aware that Domain Security is established.
Green icon with check mark will be shown on each messages exchanged between servers
on which Domain
Security is implemented.
Set-SendConnector
Use the Set-SendConnector cmdlet to modify a Send connector.
EXAMPLE 1
This example makes the following configuration changes to the Send connector named
Contoso.com Send Connector:
Sets the maximum message size limit to 10 MB.
Changes the connection inactivity time-out to 15 minutes.
Set-SendConnector “Contoso.com Send Connector” -MaxMessageSize 10MB –
ConnectionInactivityTimeOut
00:15:00
PARAMETERS
Requiretls
The RequireTLS parameter specifies whether all messages sent through this connector
must be transmitted using TLS. The default value is $false.
Domainsecureenabled
The DomainSecureEnabled parameter is part of the process to enable mutual Transport
Layer Security (TLS) authentication for the domains serviced by this Send connector.
Mutual TLS authentication functions correctly only when the following conditions are met:
The value of the DomainSecureEnabled parameter must be $true.
The value of the DNSRoutingEnabled parameter must be $true.
The value of the IgnoreStartTLS parameter must be $false.
The wildcard character (*) is not supported in domains that are configured for mutual TLS
authentication. The same domain must also be defined on the corresponding Receive
connector and in the TLSReceiveDomainSecureList attribute of the transport configuration.
The default value for the DomainSecureEnabled parameter is $false for the following types
of Send connectors:
All Send connectors defined in the Transport service on a Mailbox server.
User-created Send connectors defined on an Edge server.
The default value for the DomainSecureEnabled parameter is $true for default Send
connectors defined on an Edge server.
NOT TLSAUTHLEVEL
The TlsAuthLevel parameter specifies the TLS authentication level that is used for
outbound TLS connections established by this Send connector. Valid values are:
EncryptionOnly: TLS is used only to encrypt the communication channel. No certificate
authentication is performed.
CertificateValidation: TLS is used to encrypt the channel and certificate chain validation
and revocation lists checks are performed.
DomainValidation: In addition to channel encryption and certificate validation, the Send
connector also verifies that the FQDN of the target certificate matches the domain specified
in the TlsDomain parameter. If no domain is specified in the TlsDomain parameter, the
FQDN on the certificate is compared with the recipient’s domain.
You can’t specify a value for this parameter if the IgnoreSTARTTLS parameter is set to
$true, or if the RequireTLS parameter is set to $false.
NOT ignorestarttls
The IgnoreSTARTTLS parameter specifies whether to ignore the StartTLS option offered
by a remote sending server.
This parameter is used with remote domains. This parameter must be set to $false if the
RequireTLS parameter is set to $true. Valid values for this parameter are $true or $false.
NOT tlsdomain The TlsDomain parameter specifies the domain name that the Send
connector uses to verify the FQDN of the target certificate when establishing a TLS
secured connection.
This parameter is used only if the TlsAuthLevel parameter is set to DomainValidation.
A value for this parameter is required if:
The TLSAuthLevel parameter is set to DomainValidation.
The DNSRoutingEnabled parameter is set to $false (smart host Send connector).
NOT smarthostauthmechanism
The SmartHostAuthMechanism parameter specifies the smart host authentication
mechanism to use for authentication with a remote server.
Use this parameter only when a smart host is configured and the DNSRoutingEnabled
parameter is set to $false.
Valid values are None, BasicAuth, BasicAuthRequireTLS, ExchangeServer, and
ExternalAuthoritative.
All values are mutually exclusive. If you select BasicAuth or BasicAuthRequireTLS, you
must use the AuthenticationCredential parameter to specify the authentication credential.
TLS Functionality and Related Terminology: Exchange 2013 Help
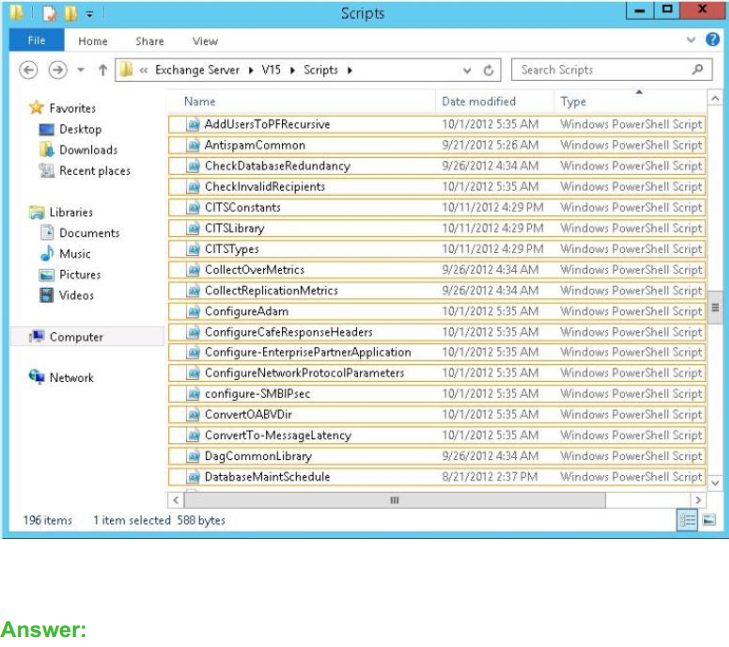
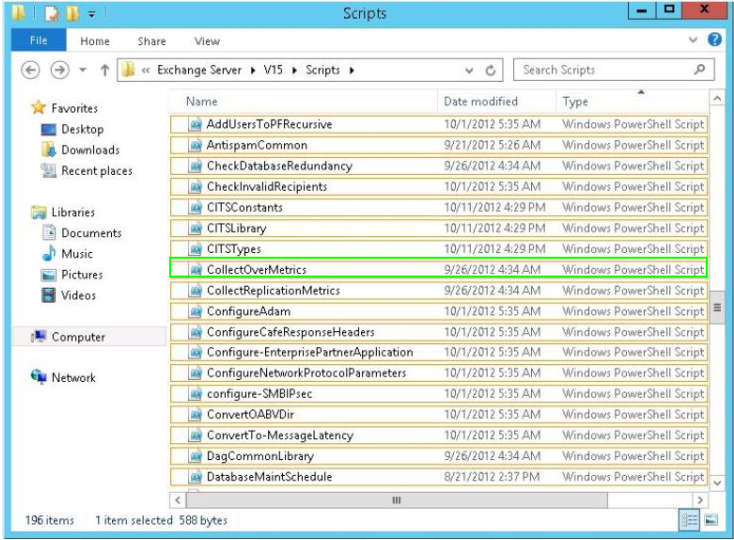
Question No : 9 HOTSPOT – (Topic 1) You need to recommend which script the administrators must run to create the reports required to meet the technical requirements.
Which script should you recommend?
To answer, select the appropriate script in the answer area.
There are too many variables and unknown temptation in life. So we should lay a solid foundation when we are still young. Are you ready? Working in the IT industry, do you feel a sense of urgency? Pass4itsure Microsoft 70-341 pdf exam training materials is the best training materials. Select the Pass4itsure, then you will open your door to success. Come on!
You have tried all kinds of exam questions when others are still looking around for Microsoft 070-341 dumps materials, which means you have stayed one step ahead of other IT exam candidates. https://www.pass4itsure.com/70-341.html 70-341 pdf software provided by our Pass4itsure consists of full exam resources will offer you a simulation of the real exam atmosphere of 070-341 dumps.